POQI-3 Infographics
British Journal of Anaesthesia
2 March 2019
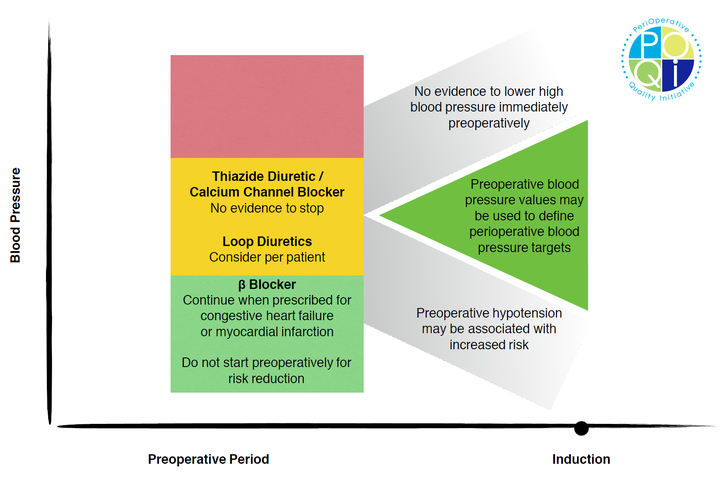
Figure 2: Infographic demonstrating the consensus recommendations from our group.
![Figure 3: This figure represents structured criteria for moving patients between levels of care based upon postoperative blood pressure. If the patient meets all criteria in the green box, then they would be cleared to move from PACU or the ICU/HDU to the ward based upon blood pressure (other vital signs or care issues may prevent such change in level of care). If the patient meets criteria in the red box, then they should move from the ward to a higher level of care, such as ICU/HDU.
*Of note, this algorithm assumes that the bedside assessment and initial management shown in Figure 2 has occurred and the patient remains hypotensive or hypertensive after appropriate initial therapies have been undertaken that are possible on the postoperative ward. [OR = operating room/theater; PACU = post-anesthesia care unit; ICU = intensive care unit; HDU = high-dependency unit; IV = intravenous; SBP = systolic blood pressure; HR = heart rate; S/Sx = signs and symptoms] Figure 3: This figure represents structured criteria for moving patients between levels of care based upon postoperative blood pressure. If the patient meets all criteria in the green box, then they would be cleared to move from PACU or the ICU/HDU to the ward based upon blood pressure (other vital signs or care issues may prevent such change in level of care). If the patient meets criteria in the red box, then they should move from the ward to a higher level of care, such as ICU/HDU.
*Of note, this algorithm assumes that the bedside assessment and initial management shown in Figure 2 has occurred and the patient remains hypotensive or hypertensive after appropriate initial therapies have been undertaken that are possible on the postoperative ward. [OR = operating room/theater; PACU = post-anesthesia care unit; ICU = intensive care unit; HDU = high-dependency unit; IV = intravenous; SBP = systolic blood pressure; HR = heart rate; S/Sx = signs and symptoms]](images/news/uploads/POQI_00690_L2.jpg)
Figure 3: This figure represents structured criteria for moving patients between levels of care based upon postoperative blood pressure. If the patient meets all criteria in the green box, then they would be cleared to move from PACU or the ICU/HDU to the ward based upon blood pressure (other vital signs or care issues may prevent such change in level of care). If the patient meets criteria in the red box, then they should move from the ward to a higher level of care, such as ICU/HDU.
*Of note, this algorithm assumes that the bedside assessment and initial management shown in Figure 2 has occurred and the patient remains hypotensive or hypertensive after appropriate initial therapies have been undertaken that are possible on the postoperative ward. [OR = operating room/theater; PACU = post-anesthesia care unit; ICU = intensive care unit; HDU = high-dependency unit; IV = intravenous; SBP = systolic blood pressure; HR = heart rate; S/Sx = signs and symptoms]
![Figure 2: This figure illustrates our recommendations for a structured bedside assessment due to perturbations in postoperative blood pressure readings. *An unstable patient would be any patient who is displaying signs and symptoms of end organ dysfunction related to blood pressure (e.g. altered mental status, chest pain). [BP = blood pressure; PLR = passive leg raise; SV = stroke volume; TTE - transthoracic echocardiography; SVR = systemic vascular resistance; ECG = electrocardiogram; PACU = post-anesthesia care unit; HDU = high-dependency unit; ICU = intensive care unit] Figure 2: This figure illustrates our recommendations for a structured bedside assessment due to perturbations in postoperative blood pressure readings. *An unstable patient would be any patient who is displaying signs and symptoms of end organ dysfunction related to blood pressure (e.g. altered mental status, chest pain). [BP = blood pressure; PLR = passive leg raise; SV = stroke volume; TTE - transthoracic echocardiography; SVR = systemic vascular resistance; ECG = electrocardiogram; PACU = post-anesthesia care unit; HDU = high-dependency unit; ICU = intensive care unit]](images/news/uploads/POQI_00691_L2.jpg)
Figure 2: This figure illustrates our recommendations for a structured bedside assessment due to perturbations in postoperative blood pressure readings. *An unstable patient would be any patient who is displaying signs and symptoms of end organ dysfunction related to blood pressure (e.g. altered mental status, chest pain). [BP = blood pressure; PLR = passive leg raise; SV = stroke volume; TTE - transthoracic echocardiography; SVR = systemic vascular resistance; ECG = electrocardiogram; PACU = post-anesthesia care unit; HDU = high-dependency unit; ICU = intensive care unit]